In a lavish list of nutritional vocabulary, it’s common to use Matcha and Maca interchangeably. Matcha or Maca- both superfoods sound alike and are seemingly similar. But, they come from completely different plants and encompass unique benefits. Matcha, a premium green tea from Japan, is made from dried, chlorophyll-rich leaves of shade-grown Camelia Sinensis plants. In contrast, Maca is a mildly sweet and malty super root from the Peruvian Andes belonging to a rare group of plants called adaptogens that aid in energizing and providing resiliency in the body.
To erase your confusion on whether a certain product is a Matcha or Maca, let’s learn more about these two superfoods in detail and their distinguishing features.
1. Matcha
- Origin and Background of Matcha
Matcha is an authentic Japanese organic green tea powder made from the finest-quality tea leaves, which are highly rich in antioxidants. The origin of Matcha traces thousands of years back when it was consumed by Eastern rulers, Samurais, Buddhist Zen monks, and even common people. It is a premium and powerful green tea powder in the purest and 100% organic form with plenty of healthy benefits.
- Defining features of Matcha
Matcha leaves are shade-grown and feature superior characteristics over conventional tea leaves. They contain more chlorophyll, higher levels of caffeine, and produce more theanine than regular green tea. The chlorophyll is responsible for Matcha’s vibrant green color and an increased detoxification capacity for the body.
Matcha contains caffeine, a highly popular psychostimulant substance that increases alertness and attentional performance. The presence of caffeine contributes to the much-touted ability of Matcha to provide clean and consistent energy and mental clarity without any crashes for up to 6 hours. Meanwhile, the caffeine amount in this highly-prized green tea is one-third of a cup of coffee. It makes Matcha a natural pick-me-up to boost your energy without cutting out caffeine completely.
Furthermore, Matcha provides more L-theanine than conventional tea leaves and offer a sense of serenity to aid your body in harnessing the full potential of caffeine over time.
- Production of Matcha powder
Matcha green tea powder is extracted from delicate, nutrient-rich tea leaves which are shade-grown and hand-picked. Upon completion of harvesting, the stem and veins are removed, but the leaves are ground into a fine powder and not steeped like conventional green tea leaves. In fact, they are steamed, de-steamed, and de-veined before being stone ground for optimum flavor and health benefits.
- Flavor/taste of Matcha
The superior-quality Matcha has a rich and complex flavor, offering a perfectly balanced palate, both sweet and earthy. It has a bold flavor profile with mellow vegetal, grassy notes, and natural sweet nuttiness; it somewhat tastes bitter but also possesses a subtle, lingering sweet aftertaste. Full of rich and savory Umami flavor, properly prepared matcha is smooth with a subtle bitter note and light natural sweetness to balance out other strong flavors.
You can incorporate versatile Matcha powder into your superfood diet in many ways. While the most popular way is to whisk it vigorously into hot water with a bit of natural sweetener, you can add it to protein smoothies, baked items, savory dishes, or even to your face mask.
- Health benefits of Matcha
Organic Matcha powder is power-packed with antioxidants and amino acids, 20 times more than steeped commercial green tea. So, it has an amazing ability to bolster your energy and system balance, keeping you composed and well-focused. Antioxidants are associated with a lowered risk of several chronic diseases as they aid in stabilizing harmful free radicals that can destroy cells. Likewise, amino acids have many therapeutic effects and help to stimulate muscle synthesis and skeletal tissue and improve brain, gastrointestinal, and immune functions.
- Matcha is nature’s strongest source of EGCG (epigallocatechin 3-gallate) which may have powerful chemopreventive anti-cancer properties.
- Matcha exhibits an impressive amount of polyphenols which confer a unique range of health-boosting properties. Polyphenols are vital micronutrients that keep your blood vessels healthy and flexible and lower heart disease risk.
- Matcha tea has a dense vitamin and mineral content; it has significant levels of vitamins A, B1, B2, B6, C, E, K, and minerals such as potassium, magnesium, calcium, zinc, phosphorus, and iron.
- Matcha is loaded with an organic compound called L-theanine that balances the effects of caffeine, giving you a slow but steady boost of energy over time.
Other health benefits of Matcha include
- Help the liver in flushing out toxins
- Enhance brain function
- Induce relaxation and reduce stress levels
- The slow growth of cancer cells
- Enhance weight loss by speeding up metabolism and boosting fat burn
Now that you have learned about the origin, appearance, taste, and benefits of Matcha, it will be quite easy to tell which superfood is which- Matcha or Maca. To learn the clear-cut difference between Matcha and Maca, let’s focus our attention on the Peruvian super-root Maca.
2. Maca
- Introduction and background
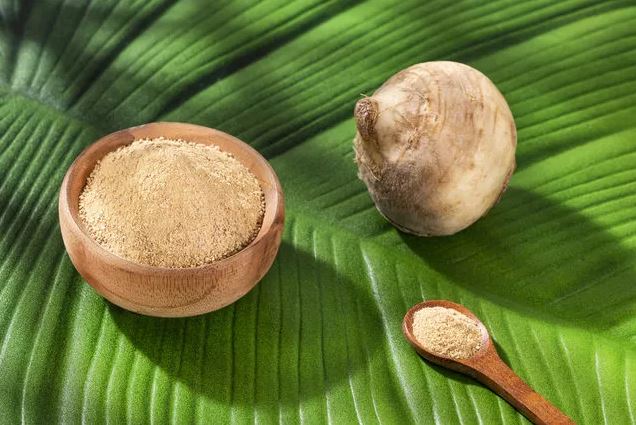
Maca is a cruciferous vegetable native to the high plateaus of the Peruvian Andes that has been used for centuries to boost energy and vitality in the body. Unlike the leaves of Matcha, the root is the most commonly used part of the Maca plant to prepare organic Maca powder. It is an adaptogenic herb that helps the body achieve a state of balance throughout by improving overall hormone function in both men and women.
Revered for centuries by ancient Inca warriors to increase energy and endurance, the demand for Maca root has spiked worldwide in recent years due to its versatile properties. The Peruvian super-root can withstand harsh weather above 4000m in the Andes mountain range and harness the very power of nature in it.
- Defining features
The most defining feature or perhaps the greatest asset of Maca powder is an adaptogen, loaded with key micro and macronutrients and stress-relieving properties to normal body processes.
Maca doesn’t contain caffeine, but that doesn’t make it less of an energy booster. In fact, it possesses natural energy-boosting qualities and helps to keep energy consistent throughout the day, without the jitters and crashes of caffeine.
It packs a major nutritional munch, rich in health-promoting nutrients like vitamins B-1, B-2, C, and E, calcium, potassium, magnesium, zinc, phosphorus, manganese, sulfur, sodium, etc.
Maca has no specific color and is available in cream, purple, gold, blue, green, red, and black-the last being the most valued one.
- Production of Maca
Owing to the plethora of health benefits offered by Maca, Peru-native Maca is now mass-produced in many parts of the world, including the Chinese Yunnan province. The natural Maca product is prepared by boiling the root or grinding it into a powder. The finest Peruvian Maca roots grown via traditional agricultural methods in Peru are harvested, low-temperature dried, and gently milled to preserve their vital nutrients. The organic Maca powder is 100% minimally processed and contains no added chemicals.
- Flavor/taste
Maca is a mildly sweet and malty super root that has an almond-like flavor when eaten raw. It has an earthy flavor with a nutty butterscotch undertone, so it pairs well with many sweeter flavors.
Traditional Peruvian people used Maca as a culinary ingredient, ingesting it in a fermented drink or porridge. Maca, as a root vegetable, is cooked to give dishes an earthy flavor. On the other hand, Maca powder is added to smoothies, oatmeal, warm drinks, baked goods, and other recipes to make a superfood elixir.
- Health benefits of Maca
- Increase libido and improve sexual function.
- Proactively support your central nervous system, adapt to life’s stressors, and bring your body into balance.
- Improve overall hormone functions; improve fertility aspect in males and pre/postmenopausal symptoms in women.
- Natural, caffeine-free energy booster
- A powerhouse of essential macro and micronutrients
Summarizing the difference between two superfoods: Matcha or Maca
It goes without saying that both Matcha and Maca are at the forefront of nutritional foods and go above and beyond to support body energy and stamina and encourage overall health. It is easy to get confused about Matcha or Maca since they sound similar. But they both have distinguishing features and health benefits which are summarized below:
- Matcha is a leafy green tea powder from Japan, while Maca is a super root from the Peruvian Andes mountain ranges.
- Matcha has a vibrant green color, while Maca has a light sandy color.
- Matcha powder has a vegetal bitter taste along with natural sweetness, but Maca powder has a nutty, butterscotch-like taste.
- Matcha contains caffeine, but Maca is caffeine-free.
- Matcha is crucial to remove free radicals from your body, flush out toxins, increase metabolism, and boost metabolism, while Maca is crucial to boost libido, improve hormonal functions, and balance stress levels.
- Matcha helps to fight cancer due to the high level of EGCG, while Maca doesn’t.
Both superfoods are organic and embrace the essence of natural ingredients, be it Matcha or Maca. They have high nutritional value and are highly popular in the marketplace. Depending upon your needs, you can consider incorporating either Matcha or Maca or both into your superfood elixir.